

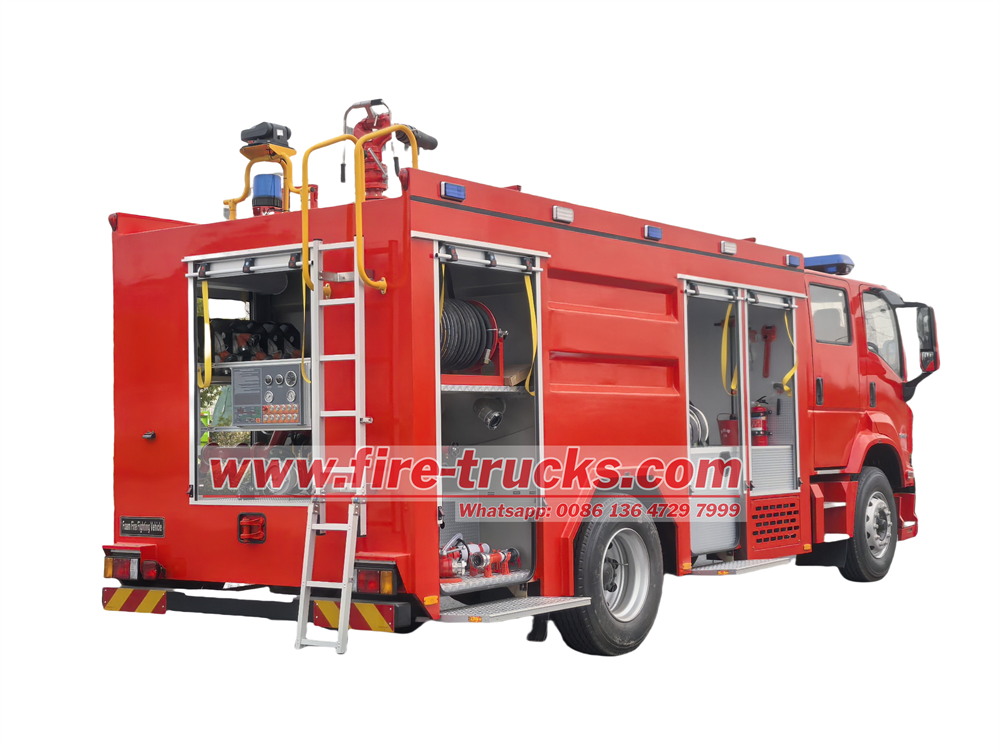
Isuzu 4,000L foam firefighting truck is engineered to combat Class B fires involving flammable liquids (e.g., petroleum, chemicals). Its foam projection system mixes water with fire-suppressing foam at precise ratios, forming an oxygen-blocking blanket to rapidly extinguish liquid fuel blazes. Equipped with a high-capacity 4,000-liter tank and a high-pressure pump, Isuzu 4,000L foam firefighting truck delivers sustained foam discharge rates up to 4,000 L/min, enabling swift control of expansive fire incidents. Its extended-range monitor nozzle projects foam over 60 meters, ensuring operator safety during refinery, warehouse, or wildfire emergencies.

Operational Guide for Isuzu 4,000L Foam Firefighting Truck: Technical Parameters and Procedures
1. Vehicle Overview
The Isuzu 4,000L foam firefighting truck is engineered for rapid response to Class B (flammable liquids) and Class A (solid combustibles) fires. Built on a heavy-duty Isuzu FVR chassis, it features a 6HK1-TCG61 diesel engine with a power output of 176 kW (240 hp) at 2,200 rpm, generating 981 N·m torque. The chassis complies with Euro V emission standards and includes a 9-speed manual transmission for optimal off-road maneuverability.
2. Firefighting System Specifications

3. Discharge Equipment
4. Control and Monitoring Systems

5. Operational Procedure
Step 1: Pre-Deployment Checks
Step 2: Engine and Pump Activation
Step 3: Foam Application
Step 4: Discharge Control
Step 5: Post-Operation
6. Safety Protocols


|
Name |
Water Foam Tank Fire Truck |
|
|
Model |
PT550PM |
|
|
Painting |
Fire red (RAL 3000) (Customer LOGO welcome) |
|
|
Chassis |
Brand |
ISUZU |
|
Chassis Model |
ISUZU GIGA 4X |
|
|
Engine power |
150KW (205HP) |
|
|
4X2 Left Hand Drive, Double Cabin |
||
|
Outline dimension |
8150×2500×3600 mm |
|
|
Gross Vehicle Weight |
18000 kg |
|
|
Number of Seats |
1+1+4 (inc. driver) |
|
|
Fire-extinguishing Agents |
Water (L) |
5000L |
|
Foam (L) |
500L |
|
|
Chemical (L) |
Without |
|
|
Fire pump |
Model |
XIONGZHEN CB10/40 |
|
Pressure (Mpa) |
1.0 |
|
|
Rate (L/s) |
40 |
|
|
Fire Monitor |
Model |
PL36 |
|
Rate (L/s) |
36 |
|
|
Throw Range(m) |
Water ≥ 60, Foam≥ 50 |
|
|
Fire Equipment |
Factory standard |
Special equipment for optional |


You may be interested in the following information