

Resce fire vehicle with 6HK1 series engine are core power systems for commercial vehicles, and sensor failures directly impact engine performance and reliability. Common fault types include abnormal vehicle speed sensor signals leading to ECU speed limits and fuel cutoffs, coolant temperature sensor reading deviations causing cooling system disruptions, and camshaft sensor failures causing ignition sequence errors. These faults are often caused by sensor aging, poor wiring connections, or mechanical installation issues (such as insufficient torque). For example, a damaged vehicle speed sensor may cause the ECU to misinterpret an overspeed condition and cut fuel injection, resulting in a sudden loss of power at high speeds.

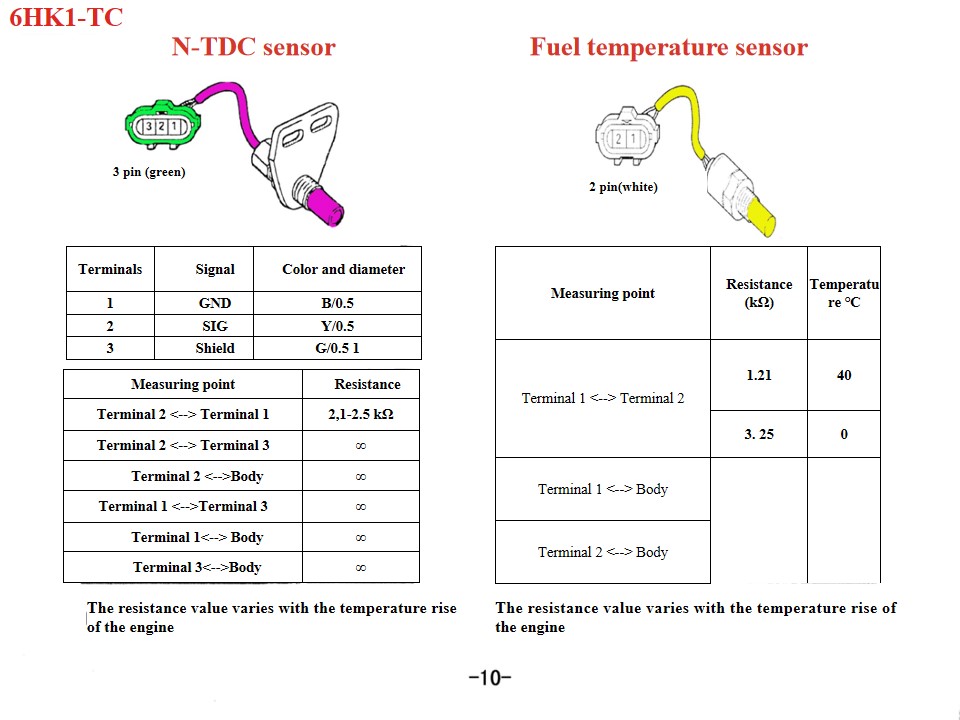
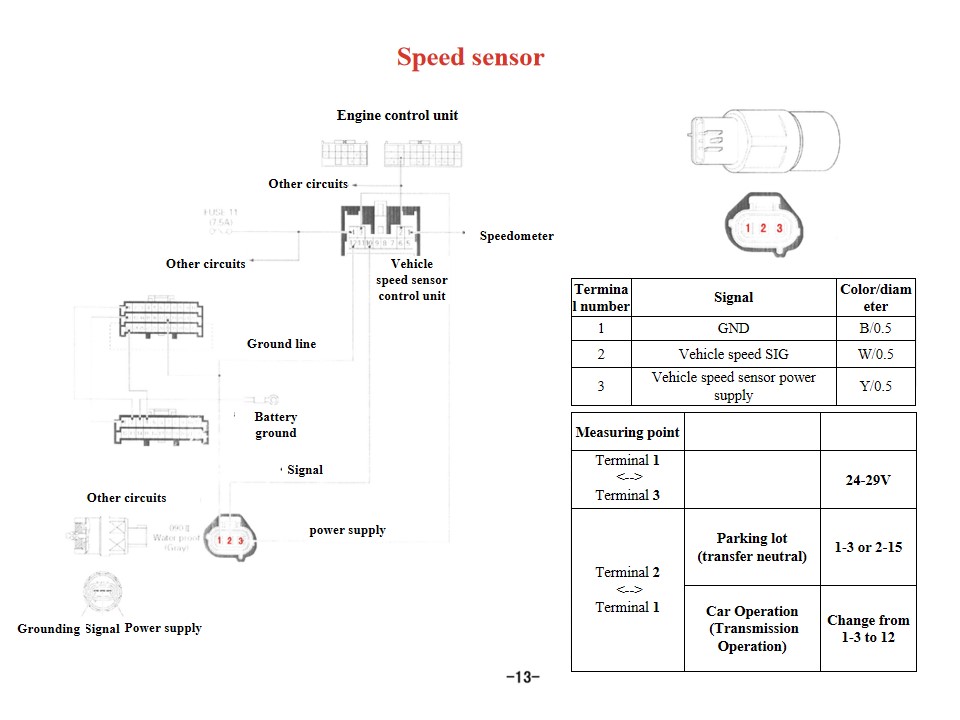
|
|
Signal |
Color and diameter |
|
1 |
GND |
B/0.5 |
|
2 |
SIG |
Y/0.5 |
|
3 |
Shield |
G/0.5 1 |
|
Measuring point |
Resistance (kΩ) |
Temperature ℃ |
|
Terminal 1 <--> Terminal 2 |
1.21 |
40 |
|
3. 25 |
0 |
|
|
Terminal 1 <--> Body |
|
|
|
Terminal 2 <--> Body |
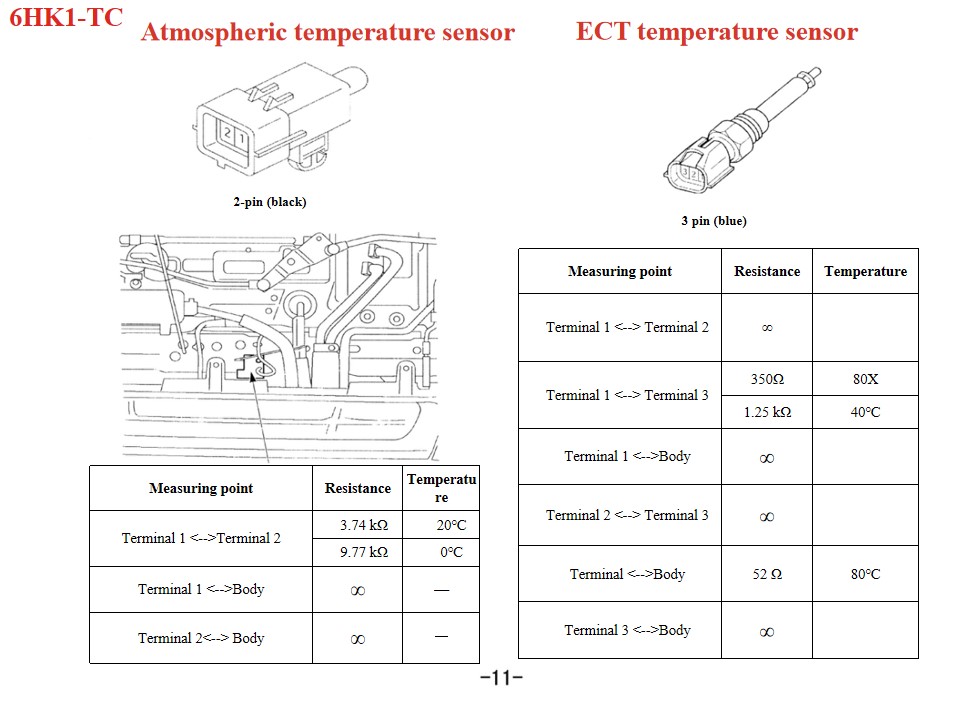
|
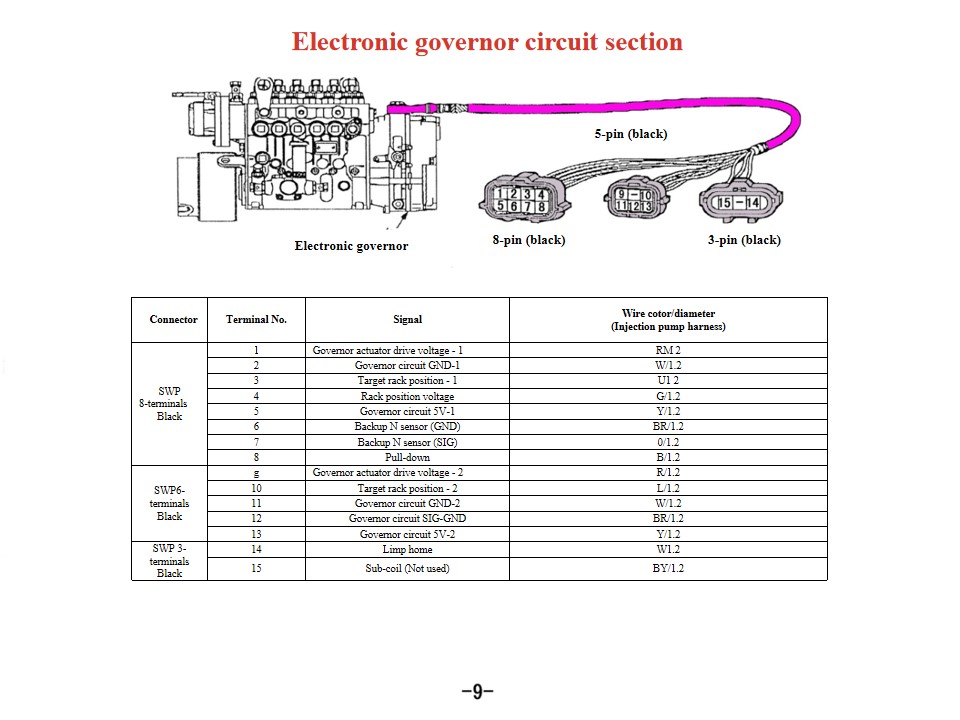
Connector |
Terminal No. |
Signal |
Wire cotor/diameter |
|
SWP 8-terminals Black |
1 |
Governor actuator drive voltage - 1 |
RM 2 |
|
2 |
Governor circuit GND-1 |
W/1.2 |
|
|
3 |
Target rack position - 1 |
U1 2 |
|
|
4 |
Rack position voltage |
G/1.2 |
|
|
5 |
Governor circuit 5V-1 |
Y/1.2 |
|
|
6 |
Backup N sensor (GND) |
BR/1.2 |
|
|
7 |
Backup N sensor (SIG) |
0/1.2 |
|
|
8 |
Pull-down |
B/1.2 |
|
|
SWP6- terminals Black |
g |
Governor actuator drive voltage - 2 |
R/1.2 |
|
10 |
Target rack position - 2 |
L/1.2 |
|
|
11 |
Governor circuit GND-2 |
W/1.2 |
|
|
12 |
Governor circuit SIG-GND |
BR/1.2 |
|
|
13 |
Governor circuit 5V-2 |
Y/1.2 |
|
|
SWP 3- |
14 |
Limp home |
W1.2 |
|
15 |
Sub-coil (Not used) |
BY/1.2 |
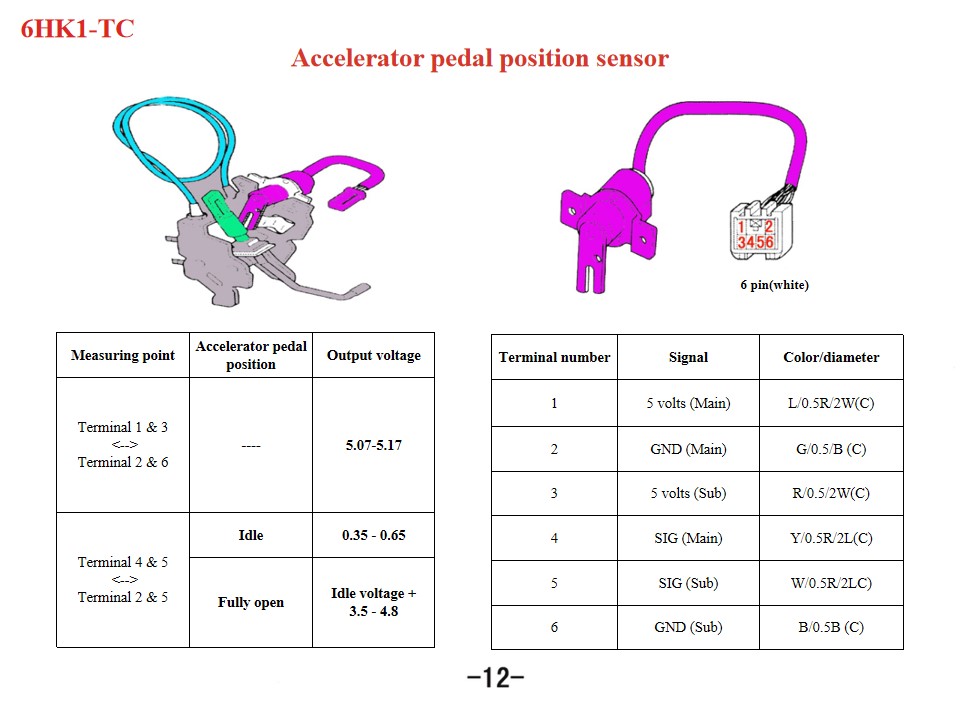
|
Measuring point |
Resistance |
|
Terminal 2 <--> Terminal 1 |
2,1-2.5 kΩ |
|
Terminal 2 <--> Terminal 3 |
∞ |
|
Terminal 2 <-->Body |
∞ |
|
Terminal 1 <-->Terminal 3 |
∞ |
|
Terminal 1<--> Body |
∞ |
|
Terminal 3<-->Body |
∞ |
Diagnosis and repair of Isuzu 6HK1 series engine sensor failures require a combination of professional testing and targeted measures. For a speed sensor failure, use a fault detector to read the data stream. If the displayed speed is significantly different from the actual speed (e.g., 222 km/h when the actual speed is 80 km/h) and the fuel injection volume is zero, the sensor is considered faulty. For a coolant temperature sensor failure, use a multimeter to measure the resistance at different temperatures.
If the resistance deviates significantly from the standard value or the signal is interrupted, replace the sensor and check the sealing gasket for leaks caused by insufficient torque. Camshaft sensor failure is often accompanied by fault codes P0340/P0341. Use an oscilloscope to check for missing or distorted signal waveforms. A clogged oxygen sensor will cause the signal voltage to be consistently high or low. Cleaning the through-hole or replacing the sensor is necessary to restore air-fuel ratio control. During repair, pay special attention to clearing ECU fault codes (such as errors caused by plugging and unplugging connectors while power is on) and ensuring the secureness of the wiring harness connectors. For widespread torque failure, optimize the gasket material or adjust the installation torque parameters. Additionally, regular fuel filter maintenance and avoiding diesel contamination can effectively prevent fuel-related sensor failures. Through systematic diagnosis and standardized maintenance, the impact of sensor failure on Weichai engine performance can be minimized.
You may be interested in the following information